Process to Qualify Products
With a multitude of WR-compatible hardwares and WR vendors, the following questions repeat:
- WR users:
- how do we know that a given WR hardware provides sub-ns accuracy?
- how do we know whether WR device from vendor A and B interoperate?
- how do we know which WR devices are proprietary and which are open-source?
- WR vendors:
- how do we test?
- how do we calibrate?
- how do we ensure that our device is compatible with other devices?
To ensure the quality, conformance and performance of products embedding the WR Technology and eventually for them to benefit of the status of Qualified Product, members can calibrate and test their products in an Associated Lab of the Collaboration to ensure their meet WR Requirements. A new and separate test shall be required for each device model and each time there is a significant update to the firmware/software/behaviour.
The scope and procedures of the tests, including the definition of “significant updates” are currently being established by the Collaboration and progressively published in this page. The same openly available and constantly refined test proceduress will be performed by all the Associated Labs.
Become a member if you would like to take part of the discussions that lead to the definition of the tests.
Details of the process and relevant documents
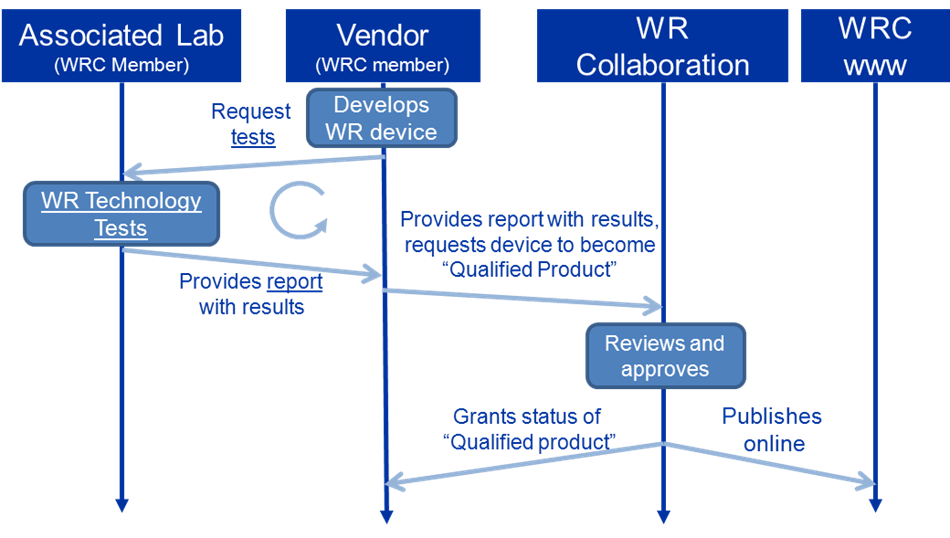
An overview of the process to obtain the status of “Qualified product” is illustrated below, in this process
- 1. A Vendor requests Associated Lab to test its device
- 2. The Associated Lab calibrates the device and verifies its compliance with the WR Requirement, a report is provided to the Vendor
- 3. The Vendor, being a WRC Member, requests that the product is granted the status of “Qualified product”, providing the test report
- 4. The WRC Bureau reviews the request and grands the status of “Qualified product”, publishing this information and the report on its website.
Documents made publicly available by WR Collaboration and relevant to the process are listed below
| Title | Version, date, link | Description |
|---|---|---|
| White Rabbit Device Requirements And Validation Methods | v1.0.0/2025.12.17(Download) | This document is a comprehensive guide to validation of White Rabbit (WR) devices. It describes technical requirements that need to be met by a device to be tested in an Associate Lab and be eligible, if it contains WR Technology, for the White Rabbit Collaboration (WRC) logo. The requirements concern interfaces, functional behaviour, standard compliance, configuration capabilities, calibration and performance, with different classes of performance distinguished. |
| White Rabbit Specification | v2.0/2011.07.06(Download,obsolete) v2.1/(to be published in 2026) | This document defines WR Extensions to IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol and WR Profile, as well as implementation details. |
| White Rabbit Calibration | v1.1/2015.11.09(Download,obsolete) v2.0/(to be published in 2026) | This document describes the calibration procedure for White Rabbit devices. |
| Auto-negotiation between HA and WR | (to be published in 2026) | This document describes methods of executing auto-negotiation between – WR Profile/extensions – defined in WR Specification – High Accuracy Default PTP Profile and optional features – defined in IEEE1588-2019 |
| White Rabbit Protocol Test Suite | (to be published in 2026) | This documents describes tests to verify compliance of implementation with the WR Specification |
| High Accuracy Protocol Test Suite | (to be published in 2026) | This documents describes tests to verify compliance of implementation with the High Accuracy Default PTP Profile and optional features defined in IEEE1588-2019 |
| Note on using WR Switch GM | 2012.10.08 (Download) | This document describes allowed relation between input 10MHz and 1PPS signals when the devices is in the GM mode |
| WR Switch FRU content specification | (to be published in 2026) | This documents provides layout of FRU (Field Replaceable Unit) required to be present in EEPROM of WR Switch |
| Achieving deterministic phase in Xilinx GTX transceivers | (to be published in 2026) | This document describes Low-Phase-Drift Calibration (LPDC) for GTX transceviers |
