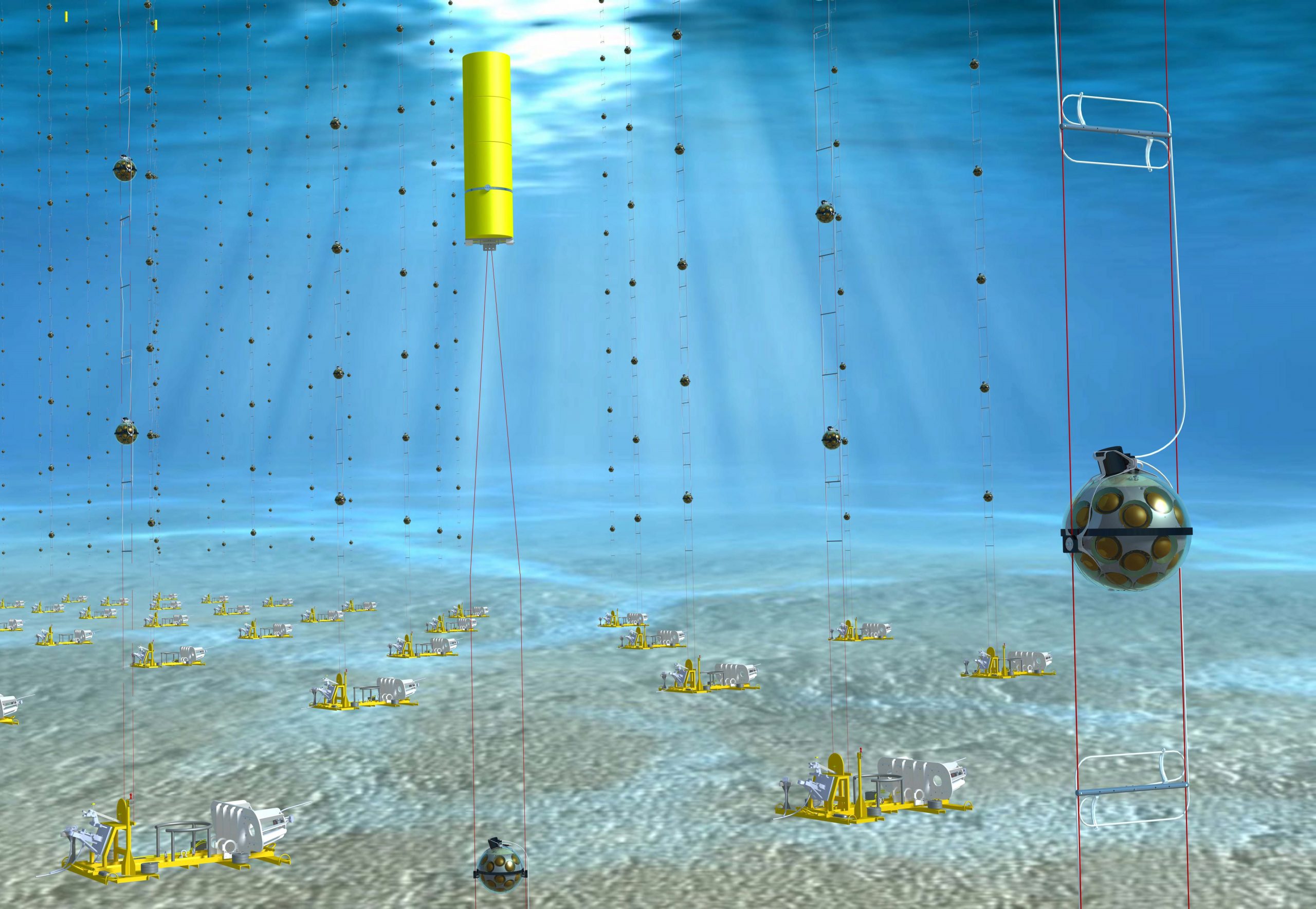
White Rabbit (WR) is used to establish a common notion of time across the network of detectors composing this underwater neutrino telescope. Nikhef has been involved in the design of many parts (mechanical, electrical and software) of the KM3NeT detector. The design of the Central Logic Board and implementing White Rabbit Technology in its FPGA is largely a Nikhef contribution.
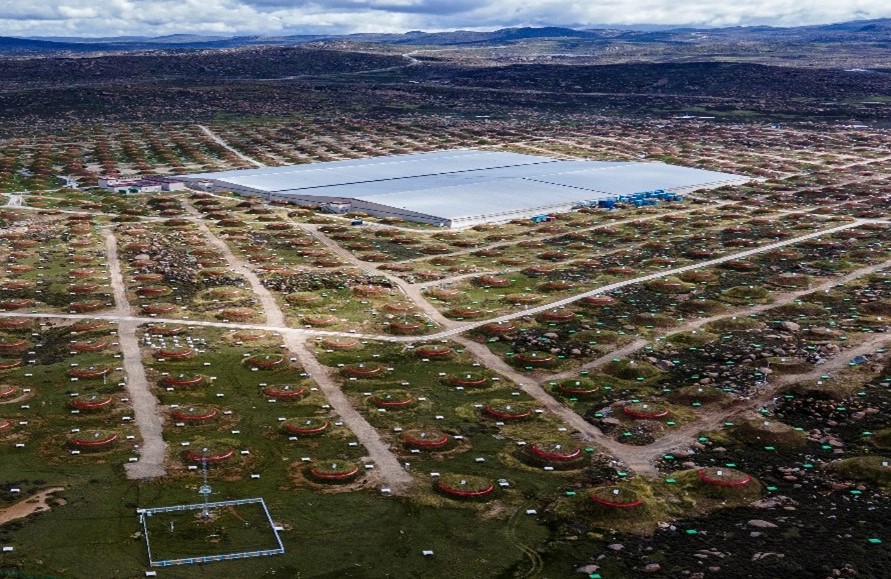

To guarantee the angular resolution of the reconstructed track of cosmic ray, the over 8000 detectors distributed over 1.3 Km2 area on a plateau of 4410 meters must be synchronized with same sampling frequency and timestamp by a clock network. WR became the key and essential supporting technology of the experiment. The WR network has been fully installed and operated since 2021.
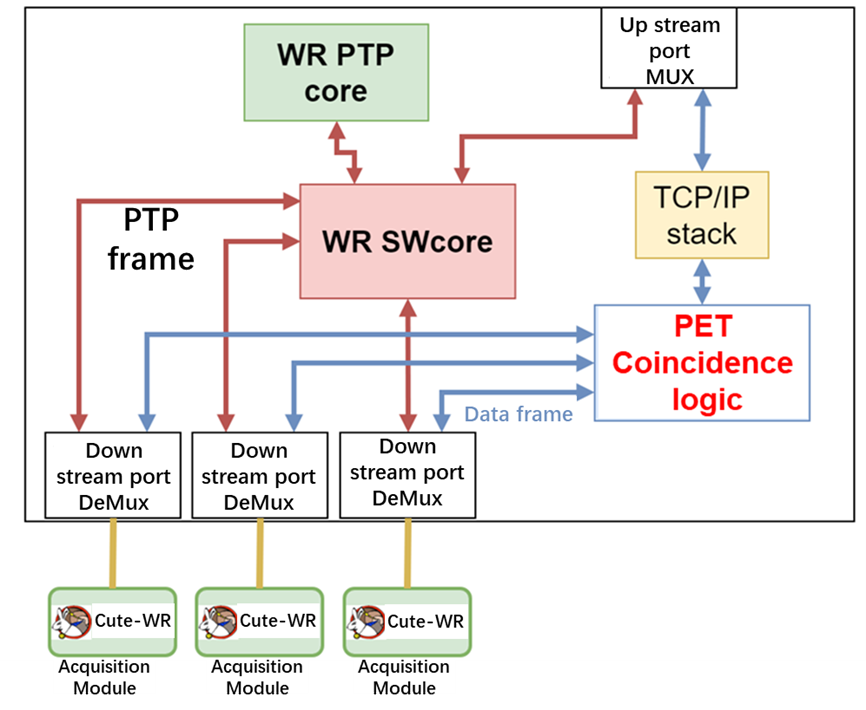
Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging is based on detecting two time-coincident photons from the emission of a positron-emitting radioisotope. With this deeply customized WR switch, an elegant and compact architecture is able to provide both time synchronization and coincidence processing and shows great scalability and modulization for PET instrument.